Enabling IT Readiness for 5G: How Network Equipment Providers can position themselves for disruption
October | 2020
Executive Summary
IT readiness for 5G business, especially for network equipment providers (NEPs), poses both opportunities and challenges. The new digital-first world forces NEPs to adapt their business models, leading to changes in their product-service offerings, governed by the demand for a holistic customer experience. The change pushes NEPs to re-think and re-build their IT organizations’ capabilities under the new normal of on-demand, scalable, and marketable solutions. Our approach focuses on the development of a new orchestration (IT capability) layer by simplifying lead-to-cash, leveraging few legacy IT functions, following specific IT design principles to minimize technical debt, and boosting responsiveness to change.
5G opportunities & New business models for NEPs
5G’s evolutionary technology will enable NEPs to tap into new revenue streams
5G has revolutionary potential through its promise of an incomparable consumer experience. This new technology will be an evolution of the existing 4G technology, with both co-existing, until 5G takes over completely.
From a technological perspective, 5G is a revolution. The imminent benefits to end-customer and enterprises will include enhanced mobile broadband, massive machine type communications, and ultra-reliable and low-latency communication.
The question that arises is whether usage and adoption will justify its investment. Both usage and adoption are highly correlated with an NEP’s business and operational model. In justifying 5G adoption, NEPs will need to evolve to one of the following models:
The NEP market landscape will change significantly with the emergence of new use-cases, new customers, and new ways of consuming products & services. The diagram below depicts the model.
NEP Marketplace
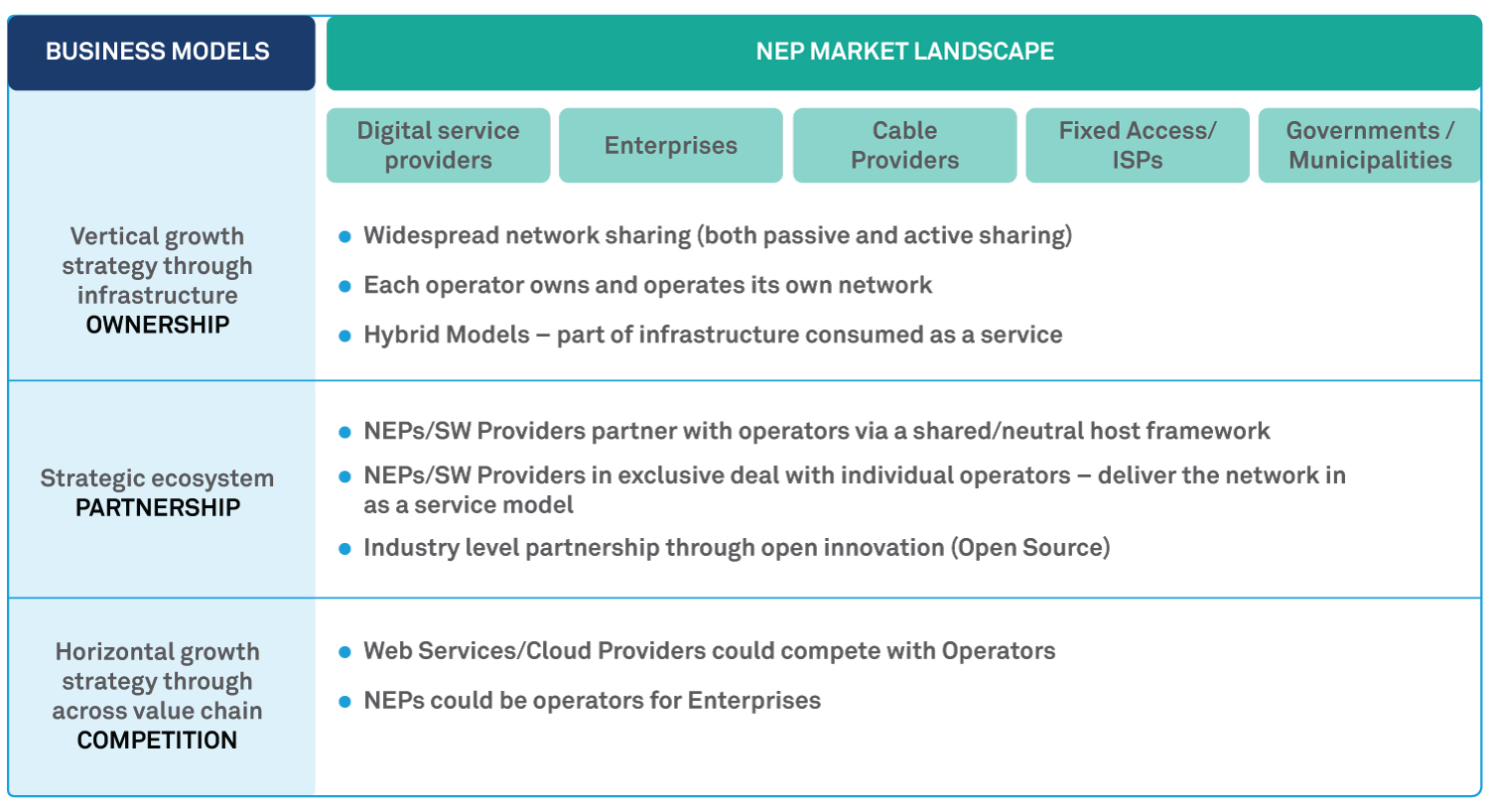
New business models bring an underlying shift in the product portfolio & service delivery
The above scenarios most likely will influence the NEPs’ product portfolio mix. Software-centric 5G network evolution will demand XaaS models, SW only product sales (from traditional HW & SW integrated product sales) and after-market services. Nevertheless, the value propositions for NEPs, described below, could solidify their market position, while driving digital transformation.
The emerging business models will not necessarily serve as a substitute for current models, but will instead co-exist with them. In that case, NEPs may act as the prime integrator where a telecom operator, subscribed or not to an NEP, would place an entire order on NEPs, which involve third-party components including software from other original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), hardware from original design manufacturers (ODMs), application vendors and security vendors. NEPs may have to work with ecosystem partners, SW vendors, and open sources to deliver products and services to customers.
NEPs could expand their portfolio services beyond their current product offering directly to enterprise. Under this scenario, use cases may include connected car (Automotive), telehealth, remote surgery (Healthcare), smart cities (Energy & Utilities), and smart manufacturing. In these markets, NEPs can extend their value proposition by bringing together vertical service providers (VSPs) and Communication Service Providers (CSP). In the vertical markets, NEPs will have an opportunity to deliver their products in SaaS models by creating an ecosystem of vertical apps and connectivity delivery solutions.
Product portfolio changes push NEPs to re-invention
Through 5G and the product/ service portfolio changes it may bring, NEPs need to revamp their external (via partnerships) and internal (via organizational structure, capabilities, and processes) strategy to align with a holistic service experience to end customers.
To retune their strategy, NEPs need to focus their resources in the following domains:
Business Strategy
Organizational Structure
IT Capabilities
Performance Measurement
Business Process
Data
The changes in the domains described above drive the NEP’s capability to create, sell, supply, execute, and deploy its revamped services. That is why a detailed roadmap is needed to orchestrate the change drivers (e.g. 5G), the impacted domains (e.g. business strategy), the impact level (low, medium, high) and the new solutions’ scalability (e.g. XaaS, exclusive partnerships). The roadmap requires a holistic approach from the NEPs and a review of the options to build their IT capabilities.
We explore four options for NEPs to build IT capabilities required to enable their 5G digital transformation:
The above options need to be evaluated against multiple criteria; however, the most relevant ones for NEPs are the following:
Speed to market
A minimal viable product (MVP) is needed fast to support 5G business within the next 6 to 12 months
Adaptability
Fluidity in the market and ability to pivot, given the unknowns of the 5G ecosystems
Enterprise grade
Fully implementable, enterprise product. The product needs to become the future core IT; no quick start-up fix
No legacy creation
Technical debt creation needs to be avoided. Architecture development and execution are of paramount importance
The Modular Greenfield methodology should be the way forward, given that incremental ‘proven’ change and rapid scaling are the most effective enablers to run IT in the digital-first world.
Key principles for NEPs to overcome technical debt of legacy IT toward their digital transformation
Irrespective of the NEPs’ chosen option to build IT capabilities to drive their digital transformation, a few practical IT design principles applied with complex legacy IT organizations of global companies need to be covered. These principles should help IT organizations improve their agility and become more responsive to business change.
Design/ Organizational Perspective
(automate, but not too much)
Technology Perspective
(execute first)
Wipro Value-Added Offerings
The following services can be provided by Wipro to facilitate the understanding and implementation of the models discussed above so that NEPs can effectively develop their 5G strategy.
Assessment of NEP readiness to offer new business models:
Define the NEP’s overall strategy:
Define new Business Process:
Develop IT Architecture:
Develop & Deploy new IT systems:
Resources:
Ravi Emani
Distinguished Member of Technical Staff
Ravi is responsible for the NEPC (Network & Edge Providers and Consumer Electronics) Practice at Wipro. He has over 23 years' experience in the Telecommunications industry and is currently working on various 5G reference solutions. He has experience in developing SW solutions in 2G/3G/4G RAN, Core, SDN, and NMS domains.
Neil Gomes
Consulting Partner, Technology Business Unit, Wipro
Neil Gomes is a Consulting Partner with the Technology Business Unit at Wipro. He has over 18 years of experience driving consulting and digital transformation initiatives, focused primarily on clients in the Hi-Tech Industry. Neil has a Master’s degree in Technology Management from Carnegie Mellon University and is also an APICS Certified Supply Chain Professional.
Themis Vagiakos
AWS Business Development Lead, Wipro
Themis Vagiakos is an AWS Business Development Lead. He has been working at Wipro since July 2019, after completing his MBA from INSEAD. Prior to Wipro, Themis was involved in business strategy, corporate finance, and business development.
Michael Quarato
Team Member, Consulting, Implementation & Product Management, Wipro
Michael Quarato is part of the consulting, implementation & product management team at Wipro. Prior to Wipro, Michael was a product design engineer in the Aerospace and Defense industry, where he designed complex systems in the radar and microwave field. Michael earned his MBA from The New York University Stern School of Business in 2019 and also holds a Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering from the New Jersey Institute of Technology in 2007.