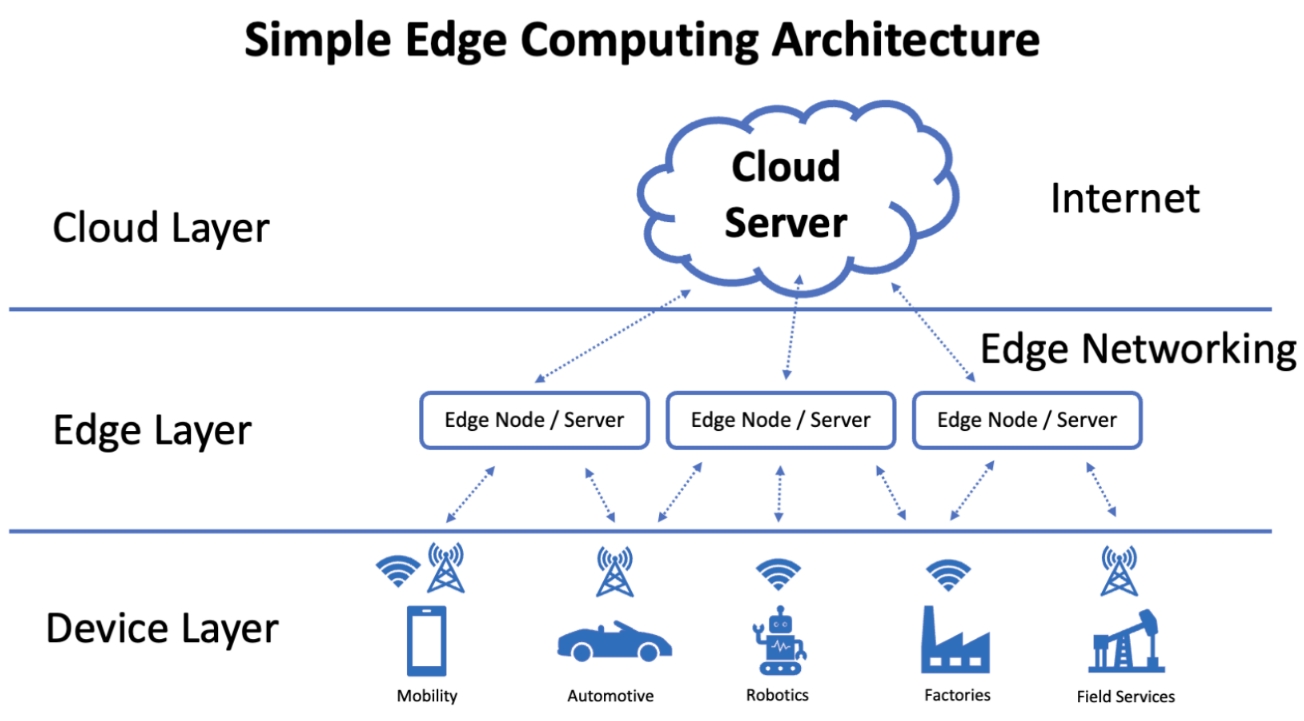
As we’ll see below, edge computing brings business and IT benefits like cost savings, bandwidth optimization, and enhanced security, all of which benefit end users indirectly. Yet edge computing also brings direct benefits to end users, including faster application response times, improved support for collaboration, greater personalization, more productivity, and a heightened user experience.
DIRECT BENEFITS TO BUSINESS AND IT
1. Maximizing Bandwidth
The need to optimize available bandwidth is critical and will continue to increase. New technologies like 5G, 6G and WiFi6 are becoming available and satellite connectivity is making progress, but the amount of data moving between points will keep rising.
Think about something as simple as the cameras in cell phones. In comparison to years past, these cameras are capturing and uploading massively more data today per photo and video. All the while, people are taking a lot more photos and videos.

In moving this increased amount of information, constant monitoring and optimization of the bandwidth utilization is required so that the end user experience remains topnotch. Through the use of edge technology, data can be processed closer to the source. Data compression and data deduplication can be used to limit the amount of data. Technologies are also available to prioritize and optimize data movement through the pipes.
2. Lowering latency
Latency is another key reason to look into edge computing. Network latency refers to the delay between when data is spent and when it is received. For most topologies, latency in the last mile is usually the highest and most impactful. The lower the amount of latency, or delay, the better the end user experience will be for interacting with applications and data. This is especially important for legacy applications and interactive applications that are more sensitive to network latency.

Here are five ways in which edge can help with latency:
3. Leveraging workload distribution
Workload distribution, an important aspect of edge computing, is about moving the workloads closer to the end user as well as spreading workload processing across a higher number of devices, zones and regions. This strategy can improve the end user experience in three ways:
4. Enhancing Security
The security of an edge computing server, if compromised, doesn’t require an entire network shutdown. In the event of an attack, it is easier for the business to shut down the affected server without disrupting the entire network. Due to the distributed nature of the architecture, work can be redirected to other edge nodes or back to the cloud.
5. Optimizing IT spending
Edge computing reduces some of the inhouse demands of traditional computing, while introducing IT hiring needs associated with the new environment. The demand for jobs like system administrators, database administrators, admin, and support functions will be affected by the improved automation, resiliency and performance brought about by edge computing. On the other hand, job roles in edge computing projects, software development, network maintenance, and analysis will see a rise.
Are there certain areas in your business where specific workloads can benefit from improved bandwidth utilization, lower latency, and workload distribution? Do you need help in understanding your current infrastructure topology to be able to plan an edge strategy?
APPLICATIONS FOR EDGE COMPUTING
Edge computing can be applied to many different workloads. Here are three of the most critical areas that companies are investigating today.
1. Manufacturing
For manufacturers who rely on data for rapid decision-making, edge computing offers an opportunity to move away from traditional data closets to a more resilient and flexible infrastructure. The data gathered through sensors and robotics can be analyzed and applied to improve processes, maintain systems, and respond to real-time issues on the factory floor.
Sophisticated sensors, for example, can improve quality control and monitor maintenance. Industrial robots can operate autonomously and communicate with manufacturing systems. Introducing or expanding the use of augmented or virtual reality (AR/VR) devices can help improve safety and training for industrial workers and reduce downtime of factory maintenance events.
How can manufacturers harness the full potential of these advanced data-driven technologies, such as the IoT, AI, and robotics, to boost productivity, streamline processes, and increase flexibility?
How can they scale the smart factory initiatives that will help them stay ahead of the competition, while maintaining data privacy and security?
2. Field services
Some examples of edge computing for field services are enterprises in the industrial, manufacturing, mining, energy, and oil and gas industries. Many of these companies are working to take advantage of the edge to let them run the core elements of their solutions locally. Local devices can save their state, interact with each other, and send important alerts and notifications. Even if the Internet connectivity goes, the edge processing in the factory, warehouse, industrial site, or mine keeps working, enabling continuity of business processes and operations.
These advantages are spurred by mobile edge computing devices that capture data directly from equipment or from sensors attached to legacy equipment. Organizations are using these edge computing capabilities to translate out-of-date machine protocols into more modern languages and interact with the modern equipment. Companies can then compute a variety of data coming in from different sensors to provide operational information with increased accuracy and reliability, or to produce intelligence that can be used for other purposes.
How can your organization utilize edge computing to run core elements of your network in local regions? Is it feasible to integrate IoT data into your edge computing solution?
3. Real-time and near real-time processing
Edge computing can minimize the network and bandwidth issues associated with moving large amounts of data to or from IoT devices and reduce reliance on the network. During edge analytics, the processing control of all applications, services, and data is then shifted from the cloud to the edge of the network, where a physical contact is made with the data source.
Edge analytics has been adopted by many vendors for use on servers, allowing businesses to pre-process their data near its creation instead of transmitting and processing in the cloud. Companies are looking to edge solutions that can process data at the source and provide summary information about what’s going on. These solutions eliminate the need for the SIM cards, data plans, and other network costs that would accrue when the data is instead transported from the device to a network. Edges can use simple logic or advanced AI algorithms to understand and build summary information.
How can pre-processing data and the increasing reliability of operations on edge technologies support your corporate initiatives? Are there areas within your business that have the ability to acquire insights faster to reduce time-to-market, operational expenses, or allow for predictive maintenance?
DIRECT BENEFITS TO THE USER EXPERIENCE
Beyond the many IT and business benefits with indirect advantages to end users, organizations are also realizing direct end user benefits that can improve abilities to attract, retain, train employees and make the workplace a more productive environment.
1. Faster response times
One of the major complaints IT organizations face from end users is the response time of the applications they work with on a daily basis. End users do not understand the underlying complexity of connecting the applications to their data, nor should they need to do so. Improving response time by bringing the various different parts closer enables employees to work more efficiently and effectively. Customers, too, obtain a better engagement experience.
The goal is to give end users the perception that their environment is close at hand, when it really might not be. Sometimes users are working with data that’s been distributed from the cloud to the edge, and sometimes the data there is thinner and optimized for their ingestion.
2. Easier collaboration
More and more of the work performed by employees does NOT happen in the siloed world of the past, where one person creates something for someone else to consume independently and serially. Organizations are uncovering an increased requirement to use technology to enhance collaboration, especially with the rise in remote work since the pandemic. Edge computing enables and enhances collaboration by allowing for faster and thinner data access.
At the same time, technologies like augmented reality/virtual reality (AR/VR) in the workplace are allowing for real-time collaboration in the workplace, in contrast to approaches of the past which were limited to audio communication at best. Solutions like Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) and engineering VDI (eVDI) or graphical VDI empower users to share information rapidly and quickly by minimizing the movement of data. Combining those technologies with edge can reduce the networking path, enhancing end user experience and significantly improving end users’ perception of the ecosystem.
3. Individualized experience
Finally, by bringing edge technologies closer to end users and customers, businesses can offer more personalized experiences. These can include improvements in the collection of information such as customer sentiment while shopping, for instance. Improvements in data collection can lead, in turn, to greater efficiencies in supply chain and distribution.
It's possible with edge technologies to create regional, local and even personal experiences for users. The data and the people can be nearly co-located, with no need to keep connecting back into the cloud and/or the datacenter.
What are the best ways for your organization to harness the power of edge computing for improved collaboration, personalization, productivity, and satisfaction? Are you looking at incorporating live streaming video, AR/VR, or VDI into your edge computing solution?
SUMMARY
Edge computing opens up new worlds for improving the user experience through faster application response time, bandwidth optimization, reduced latency, and better support for personalization and remote collaboration. Edge also provides an optimal environment for innovative new technologies such as live video streaming, VDI, and AR/VR.
The results? Improvements to business processes, productivity, and employee and customer acquisition and retention. After all, ultimately, edge computing is about the end user.
To learn more about Wipro’s approach to Accelerating Your Innovation, visit Innovation.
Nicholas Holian
Global CTO and GM,
Wipro FullStride Cloud
Nicholas Holian serves as the Global CTO and GM for Wipro’s FullStride Cloud business unit with a focus on customer growth strategic transformations using new and emerging technologies and methodologies. Nicholas has been helping customers understand how to take advantage of cost savings, automation, cloud and other technologies to accelerate their business transformations to meet their customer demands.