eMBMS (Evolved Multimedia Broadcast and Multicast Services) is a mobile wireless technology that enables transmission of multimedia content broadcast over the 4G LTE licensed spectrum. Over the years there has been an increase in multimedia content consumption. It began with analog broadcast and then progressed toward digital broadcast, video on demand, podcast, and live video streaming. Since the onset of cellular technology there has been a constant attempt to provide seamless user experience of multimedia content. In the many years of mobile technology existence, many attempts have been made in defining and deploying technologies that enable seamless user experience of multimedia content, nevertheless none of them gained the success that were thought through. eMBMS is another effort by 3GPP to achieve this.
The uniqueness of eMBMS is that it can transmit data in both unicast (dedicated channel between one sender and receiver) and multicast (one sender to multiple receivers) mode. This gives operators the option to realize rapid scalability and huge network efficiency gains (when transmitting through multicast mode) while delivering high quality voice and data services (when transmitting through the unicast mode).
This paper explores the possibility of eMBMS becoming the standard technology platform for transmission of multimedia content over cellular networks. It details out the advantages of adopting eMBMS and the various scenarios in which it can play a game-changing role.
Why eMBMS?
Multimedia data can be received by a device in “Unicast” or “Broadcast / Multicast” mode. “Broadcast / Multicast” mode has several advantages over Unicast mode.
Unicast mode:
Media is transported on a dedicated radio and core network connection. It’s a point-to-point means of communication, ideal to deliver quality service for real-time voice and video communication, web, email or social media, and on-demand video streaming.
Broadcast / Multicast:
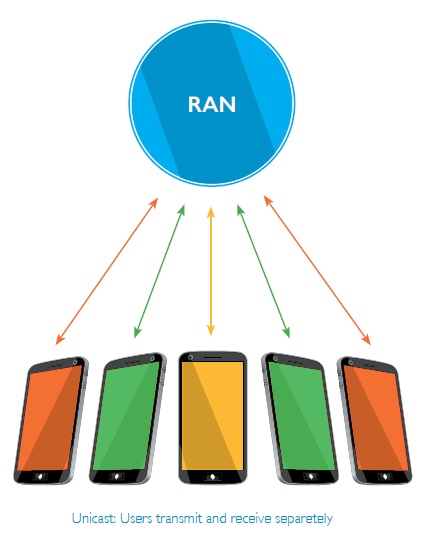
Figure 1: Unicast Mode
The uniqueness of eMBMS is that it can transmit data in both unicast (dedicated channel between one sender and receiver) and multicast (one sender to multiple receivers) mode.
Some of the advantages of eMBMS include:
Highlights of eMBMS
1. Same infrastructure as used for LTE, with new network elements added – providing means of cost effective upgrade to the current LTE deployment
2. Using the same spectrum as LTE, eMBMS can reach scalable number of subscribers
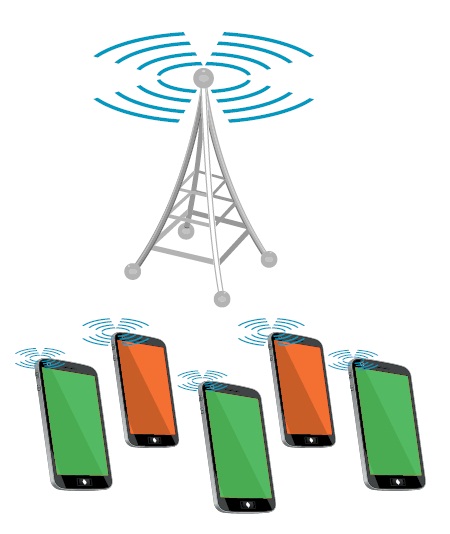
Figure 2: Broadcast Mode
3. Optimization layer of LTE, allowing for an extremely efficient distribution of popular content
4. Unlike many other broadcast technologies, eMBMS enables the same LTE / User Equipment Terminal to be used for mobile broadcast reception
1. Flexible allocation of radio resources, with possibility of up to 60 percent of an LTE frequency carrier dedicated to MBMS transmissions
2. Flexibility to use unpaired spectrum with paired spectrum. With spectrum being a scarce resource, this would help service providers
3. Flexibility to dynamically switch between unicast and multicast mode
1. MBSFN (Multicast-broadcast Single Frequency Network): Enables better reception due to inherent gains from OFDM. Also mitigates cell edge spectrum efficiency issues
2. MBSFN area: Area over which same multimedia content is delivered synchronously, enabling possibility of localized broadcast
3. Provision of having a longer cyclic prefix - Enabling longer cell radius, can reach more subscribers
4. Interaction with user is possible due to presence of Uplink channels
Applications of eMBMS
Video or multimedia content is a data intensive application that service providers or network operators are gearing up to reap benefits. But these benefits do not come without challenges. The key challenge is to cater to this ever increasing demand. Operators need to increase their capacity several folds from across radio access to the entire backbone. Further, the mass scale adoption of OTT applications drains high resources of service providers as the content is delivered in unicast mode.
eMBMS offers means to efficiently use the resources and reduce the need for transmitting the same content over several pipes / bearers to multiple consumers. In addition to this, eMBMS also offers the flexibility to switch between broadcast and unicast mode dynamically. Consumers will benefit immensely as their data charges will drop significantly. Multimedia consumption over mobile networks will no longer have to fall under a regular data plan but can be bundled in a cost-effective service plan. Here are some areas where eMBMS can be of immense benefit to consumers, network operators and governments.
With the increased proliferation of smartphones and tablets, consumption of multimedia content has been on the rise. Coupled with this is the fact that people are spending more time travelling than ever before (people commuting to work places in urban cities spend two to three hours each day travelling). This presents a huge opportunity to network operators. How can operators keep consumers engaged during long commute times?
1. Mobile TV (Linear TV)
eMBMS allows network operators to efficiently deliver television content or live television at much lower cost through its broadcast mode. Operators can offer these television channels to customers for free without cutting into their data plans.
2.Video on Demand
With personalization in multimedia consumption catching on, eMBMS can play a big role in facilitating video on demand. As several users request to watch similar content (highlights of games, repeat broadcast of season finales or popular shows), the multicast mode can be used to push content to multiple users at the same time. This will help free up huge network bandwidth.
3. Localized Broadcast
eMBMS services can be controlled to a MBMS area, providing the option of broadcasting localized content. For instance, locationbased services updated in real-time such as traffic reports, parking locations, etc.
4.Event Coverage
Events are always an attraction, be it sports events like soccer games, or celebrity performances. As large audience like to tune into these events, eMBMS provides a perfect way to deliver live content to multiple consumers. In addition, replays or live recordings of popular events can also be presented to consumers on-demand.
LTE broadcast can progressively replace traditional FM delivery and provide digital quality audio together with new multimedia content. The reach of network operators is much wider than the current FM Digital radio coverage. eMBMS with its superior technology can also extend its coverage by using a longer cyclic prefix, enabling larger cell radius and covering more subscribers. Additionally, localization of content is also possible for different geographies.
eMBMS provides means to effectively reach today’s tech-savvy customer who is always “online” using smartphones. Operators can provide businesses with much cheaper alternative to deliver multimedia content / ads to millions of users who are on their network. For instance, video ads - promotion of movie launch, teasers to events and audio ads - promotion of new albums or songs, etc.
Emergency situations usually place a huge demand on communication systems jamming the systems causing inconvenience to all. eMBMS enables broadcasting critical lifesaving information to all and can be received by each on their personal devices immediately, reducing stress on the networks.
Firmware or OS updates are a need for smartphones or tablets, with each mobile vendor providing updates to correct issues or add new features. eMBMS broadcast can deliver firmware updates to millions of users simultaneously.
The number of IoT devices is set to explode. Internet of Things or M2M is expected to connect devices seamlessly to a central server or cloud. Though most of the IoT devices are expected to consume low data packets, the sheer number will outweigh the available network capacity. eMBMS can enable efficient transmission of common configurations, commands, software updates to multiple devices. eMBMS provides the mechanisms or configuration options by which IoT device of an enterprise could be addressed independently by way of localization. Use cases like street light on and off would need extremely minimal signaling as against the existing unicast mechanism.
Conclusion
Data consumption in mobile networks is on the rise with the spectacular proliferation of smartphones and tablets. eMBMS is one way of providing new services to multiple users in an efficient way maintaining the Quality of Service, enabling multiple new revenue streams for operators. Use Cases discussed above have different potential in different markets. In this age of connected homes, connected cars, and the Internet of Things in general, eMBMS is definitely better positioned than LTE to address the vast network demands and challenges.
eMBMS benefits of wide coverage, efficient utilization of resources and standardization across geographies and platforms, makes it an attractive solution. Although eMBMS has all the aspects that could revolutionize multimedia broadcast, it is not just the technology that would make it an industry standard. Larger factors such as cost, concurrence across the entire network ecosystem and deployment challenges will play a part in determining the success of eMBMS. These factors are discussed in detail in the next part of this three part series – “The eMBMS Puzzle: A look at the challenges”.
Vishnu Vardhan Kandan is a Senior Architect in Modem & Wireless Communication Systems at Wipro.
Vishnu comes with over 17 years of experience in the wireless industry. He has worked across the entire software development lifecycle of cellular modem in 2G & LTE roll-outs as well as in M2M communication.