The insurance industry has traditionally relied on data sources such as claims history to underwrite known and measurable risk. A new wave of global challenges – financial crises, economic uncertainty, geopolitical shifts, and climate change – has introduced an elevated level of risk exposure in the insurance industry.
These new risks are less predictable and difficult to quantify, and include factors like inflation, supply chain disruption, accelerating cyber-attacks, an abrupt restructuring of business models, extreme weather, increased litigations, the rise of the gig workforce, new regulations, and changing consumer behavior.
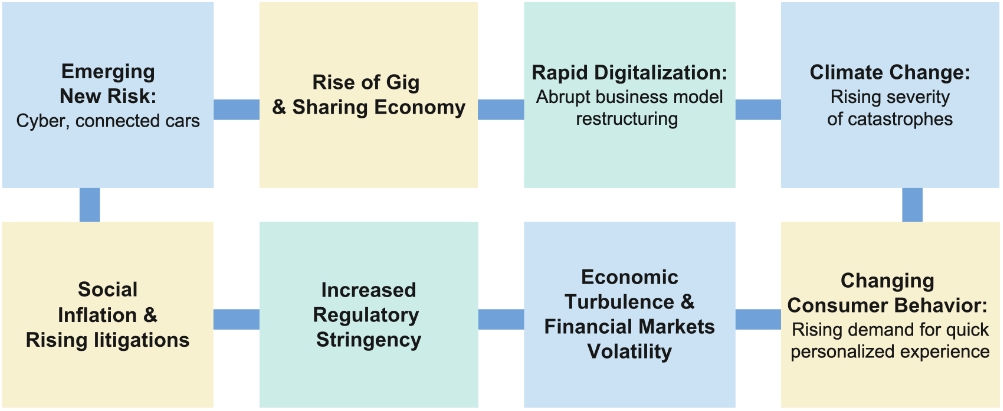
Figure 1: New and changing risks faced by insurers. Source: Wipro Insights Analysis
To tackle these rapidly evolving risks, insurers require a comprehensive and dynamic analysis of the economy, market, and several other risk-generating parameters. This dynamic analysis substitutes static assumptions with data-driven, real-time knowledge, and generates actionable insights that insurers can leverage to mitigate risk.
Data is the cornerstone strategic asset in conducting this dynamic analysis. It is imperative that insurers harness their data to remain customer-centric, drive new products, and achieve competitive advantage. However, it can be difficult for established insurers to transform into data-centric, data-driven organizations. The primary challenge is collecting relevant data in real time, and storing it in an enriched, structured format. Legacy systems, aging infrastructure, and in-house talent constraints further exacerbate the challenges faced by insurers. Furthermore, the benefits of moving toward a more data-driven approach are never immediate, and require a long-term ROI perspective that can be difficult to maintain when budgets are squeezed.
Adopting a holistic data framework to address data-related challenges
A holistic approach is required to implement end-to-end data transformation and gain agility, efficiency, and automation across the insurance value chain. This can be achieved by deploying/modernizing a four-stage data framework that considers how to source, structure, store, and synthesize data (see Figures 2 and 3).
Sourcing: Insurers will drive greater value and insight if they can leverage data from both internal and new external sources. For instance, they can source data generated in real time by connected IoT devices such as smart watches, vehicle telematics, and industrial IoT sensors, as well as by drones and satellites. Moreover, insurers also have large volumes of internal data, generated over time but buried in departmental silos, which could be further leveraged through operational integration across verticals.
Combining internal data with data from new sources is a strategy that can act as a force multiplier in delivering a remarkable competitive edge.
Structuring: The large volumes of data collected across internal and new sources come in different formats and require structuring to be rendered usable. It is vital for insurers to have effective structuring tools and platforms in place, as this will determine the quality of data, thus directly impacting the accuracy of insights and outcomes.
Storing: Storing data on cloud servers and integrating it with other insurance operations is key for effective data transformation. While the cloud had become widely leveraged by insurers to store and retrieve data, only a limited number of insurers have integrated data from across functions. Moreover, many have not fully integrated the cloud with their operations and have not fully leveraged the potential of cloud for data transformation.
Synthesizing: In the end, value is derived from effectively synthesizing data. Data processing technologies such as advance analytics, AI/ML, cloud computing, and blockchain will equip insurers with the capability to effectively analyze data and derive actionable insights.
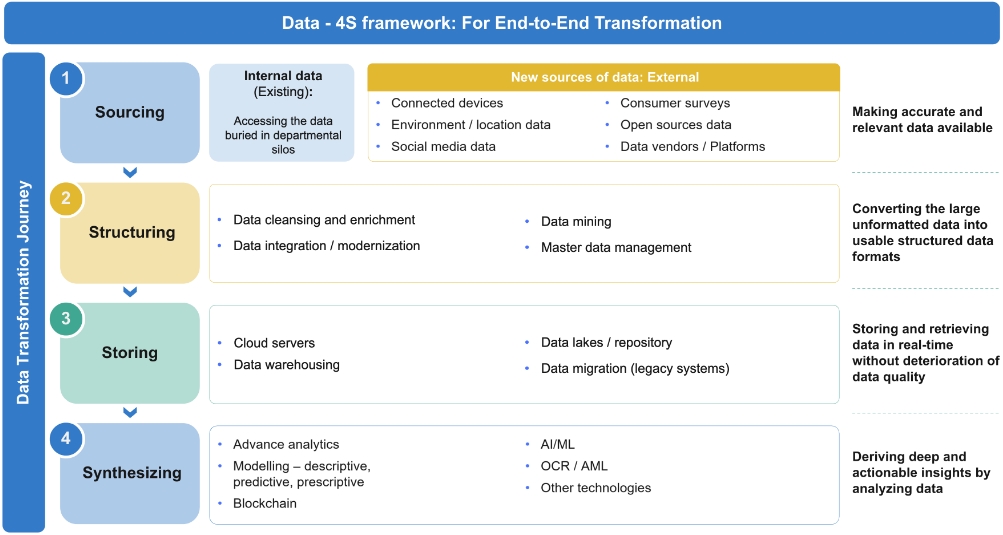
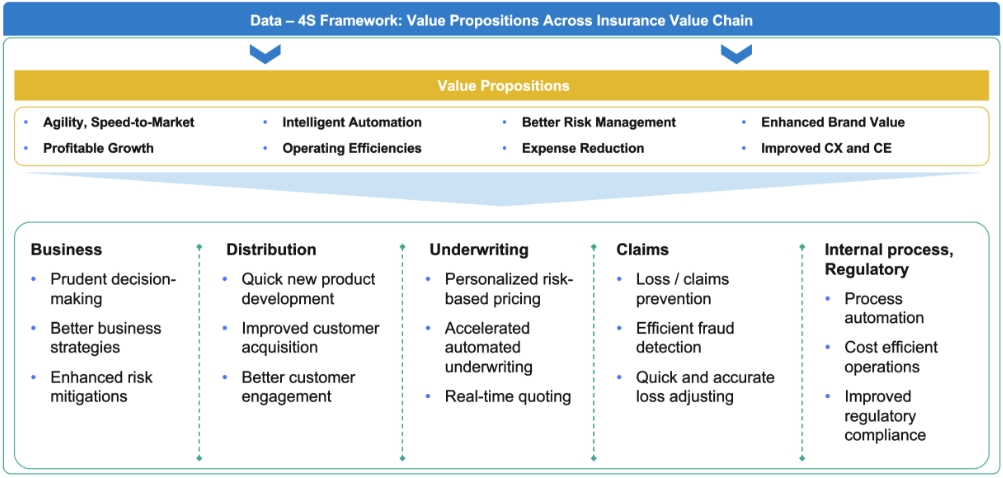
Figure 3: Value propositions of the data: 4S Framework Source: Wipro Insights Analysis
With a holistic data ecosystem in place, insurers will begin to unlock the full value of advanced data-driven operations.
Data use cases: How data can create value and impart a competitive edge
Underwriting automation: While insurers will continue to manually underwrite complex, high-value risks, they can already automate the underwriting of simple risks by leveraging data and straight-through engines to enable real-time risk assessment. Automation enhances the customer experience by accelerating processing times, while also resulting in operational cost efficiencies. For instance, we have seen a commercial insurer leverage multi-source data and apply advance analytics to process more than 15% of its new business through automated systems, thus strengthening its position in the commercial segment. In another case, a life insurer reduced underwriting expenses by up to 20% by adopting data-driven automated underwriting.
Loss prevention and fraud detection: Real-time data from IoT devices enables insurers to continuously monitor customer risk exposure and adopt preventive modelling to notify them before the occurrence of loss. Moreover, in cases of loss occurrence, IoT data plays a significant role in conducting accurate loss assessment and quick claims settlements.
For instance, we have seen a midsized insurer leverage IoT data to avoid property losses due to frozen pipe leaks, reducing its loss ratio by more than 4%. Similarly, another midsized insurer that offers policies to restaurants used IoT sensor data to trigger preventive measures when electrical outages threatened to spoil refrigerated goods. A large personal lines insurer, meanwhile, is leveraging data from social media to identify fraud, and several commercial insurers have already deployed drones and satellite imagery to estimate catastrophe losses and crop damage.
Profitability: Insurers can also leverage data to lower their risk exposure and increase profitability through simple behavioral nudges. One life insurer is extensively using health-related data collected from smart watches to track customer health risks and then reward them for adopting healthy lifestyle choices. Several motor insurers have begun linking driving behavior with premiums, thus nudging customers to follow safe driving practices to earn discounts and rewards.
Claims digitalization and automation: Increasingly, data-driven core platforms will enable insurers to fully automate most low-complexity claims, particularly in their personal lines. An end-to-end touchless claims journey will begin when the end customer uploads imagery and proof of damages through an app, while image recognition and AI/ML will be used to assess damages, identify a repair provider and schedule a repair. More broadly, algorithm-based claims segmentation will separate automatable claims from claims that require hands-on adjuster attention. Furthermore, the role of the adjuster will shift, which will require significant talent transformation. As adjusters become more data-driven and iterative, they will leverage advanced data-management skills (rather than process-related skills) to efficiently handle complex claims.
Conclusion: Transforming into a dynamic, data-driven insurance organization is critical to 21st century success
While the COVID-19 pandemic was a shock to the system for insurers, the waning of the pandemic is not bringing a return to business as usual. Some of the changes in market dynamics and consumer behavior that were triggered by the pandemic are becoming permanent, and new global risks are impacting insurance underwriting and business models. Considering this backdrop, it is crucial for insurers to integrate a comprehensive data framework and strategy into their business models, making themselves future-ready and able to confront an evolving risk landscape.
Data practices will become even more critical as trends like embedded insurance become more pervasive. Data security, privacy and access – as well as data portability and consent management – will become defining areas for building customer trust as sensitive data is shared and stored within extended enterprise ecosystems.
The insurers that harness the full potential of data will be able to tackle the emerging risks and gain a durable competitive edge over insurers that lag in data adoption. Companies slow to adopt new data practices are certain to face sustainability challenges and gradually lose market share, not only to efficient data-driven incumbents, but also to agile new entrants who are eager to capture their own share of the 21st century insurance market.
Industry :

Suzanne J. Dann
CEO - Americas 2
Suzanne Dann is Wipro's CEO for the Americas 2 region and is also a member of the Wipro Executive Board. She leads the Financial Services, Manufacturing, Energy and Utilities, and Hi-Tech sectors, as well as Wipro in Canada.
With over 25 years of experience in consulting and technology services, Suzanne has held multiple leadership positions at both IBM and Avanade. She joined Wipro in April 2021 as the Senior Vice President of Capital Markets and Insurance, successfully leveraging her deep industry expertise to deliver growth and build a high-performing team committed to client success. Suzanne also serves as the Executive Sponsor for Americas 2 Diversity and Inclusion initiatives.
Suzanne holds a B.S. degree in Engineering from Cornell University and a CISSP. She currently resides in New Jersey with her husband and their two children. In her free time she enjoys hiking, golf, and traveling with her family.