September | 2020
Financial institutions have been slow at adopting cloud technologies primarily due to concerns around security, regulatory compliance, and governance. As a result, they have been facing business model-related challenges like legacy technology, high running costs, and lack of scalability.
Adoption of cloud is becoming the norm now and analysts expect about 75% of the financial institutions’ infrastructure and data to be processed in the cloud by 2022.
In this paper, we will look at the current needs of Banking, Capital Markets and Insurance industries and how moving to cloud helps them build the foundation for digital transformation.
Financial institutions: The changing paradigms and needs
Banking
Banks have been evolving to business models that are digitally focused. They are having to do so as “digital-only” banks are tapping into their market, offering consumers digital banking tools such as mortgage calculators.
Traditionally, customers have gone to the megabanks to obtain access to different banking accounts that offer flexibility in areas such as overdraft fees. This is no longer the case as the digital-only banks now offer checking account services while providing competitive overdraft fees. Megabanks are having to adapt their business models to catch up.
Previously, business models relied on the customer looking at the number and location of branches to bank with. As we see now, across all income levels, branch location is not a significant factor.
The rise in digital banking and innovation requires banks to offer services to their customers at an affordable unit product cost without impacting operational efficiency. Technology and data platforms that are versatile and instant are paramount.
Capital Markets
High capital expenditure costs on technology have for long constrained the capital markets industry. A standard use case has been around the buying and selling of trades that can rapidly increase/decrease during peak hours in real-time. The collection of trade data and the need for real-time analytics has traditionally meant expensive technologies deployed in data centers that provide permanent, extensive processing capabilities even though they are only required during peak hours. Besides, large IT teams need to be on standby during these peak hours to ensure platform availability in the event of an issue.
Insurance
Let us focus on an example within the Property and Casualty (P&C) Insurance industry. Traditionally, claims management has involved customers interacting with call centers over phone calls (single channel) and then completing paper-based forms sent by post/emails. The claims process has been known to take several weeks involving multiple phone calls, leaving the customers with a negative experience. According to the Claims Journal, claims servicing within the P&C industry has the lowest positive experience across all insurance lines of business. Yet, it is the most crucial factor in customer retention. Millennials use multiple channels to communicate. Enabling an omnichannel approach has become the norm for creating an integrated customer experience, leading to their retention.
Financial institutions are facing issues with expensive legacy platforms, the growth of digital / omnichannel demands, and the need to process vast volumes of data in real-time. All of this is occurring at a time when they are looking to reduce IT spend to focus on delivering value to their customers.
The drivers of cloud adoption
Financial institutions are looking for technology and data platforms to support their focus on the customer. We will use the P&C Insurance example cited earlier to illustrate the drivers of cloud adoption in insurance. The three key drivers are:
1. Move from CapEx to OpEx models
Taking the P&C Insurance claims example, traditionally, being able to grow business across geographies has required high upfront CapEx. Moving to cloud-based technologies frees organizations from such constraints. They can adopt flexible OpEx models that can free financial institutions to focus on driving innovation and delivering excellent customer experience.
2. Deliver digital customer experience at minimal cost
Digital banks, with their innovative and connected customer experience, are successful in driving customer acquisition, new marketing opportunities, retaining customers, and growing revenues. Therefore, technologies and data platforms need to be digitally scalable in engaging customers without introducing massive cost base. Again, taking the P&C Insurance claims example, the millennials are expecting:
Financial institutions need to provide their customers with on-demand technology to meet their demands better.
3. Be elastic to meet changing customer demand
Increased number of customers and demand for immersive experience add complexities within the banking infrastructure. It gives rise to the need to address continuous explosive data growth at the same time adhering to higher service level objectives and agreements. Typically, when demand is lower during non-peak hours, the cost of technology usage should also reduce. As in our P&C Insurance claims example, the need of omnichannel approach means that peak hours are becoming more varied (unlike fixed opening and closing times of traditional call center) and require significant compute power at different times throughout the day.
Toward digital transformation with cloud
Financial institutions’ have stepped up their pursuit of transformation in the age of Industry 4.0 and digital disruption. To become an Intelligent Financial Hub, business thinkers are looking for possibilities and changing their existing business models through the vast amount of information integrated across various sources. Cloud ecosystem unlocks financial institutions’ capability to manage and mine massive scale datasets of their users involved in billions of transactions. Figure 1 depicts how cloud is disrupting the evolution of the financial institutions.
In addition to digital customer experience, financial organizations are disrupting and introducing new products and platforms. Let’s consider how cloud is changing the claims business model for insurance. Sophisticated machine learning-based fraud detection models can crunch through large volumes of varied data such as photos of the damage, previous customer claims, social media status etc. to assess fraudulent claims. This allows effective “Auto-Approvals” of claims as well as the identification of ones that need “Manual Investigations”. It speeds up the overall claims time, improves accuracy, and results in higher retention rates.

Figure 1: Cloud-native financial institutions
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS) are the backbones of cloud offerings. Figure 2 shows how many data services are being deployed using these cloud offerings.
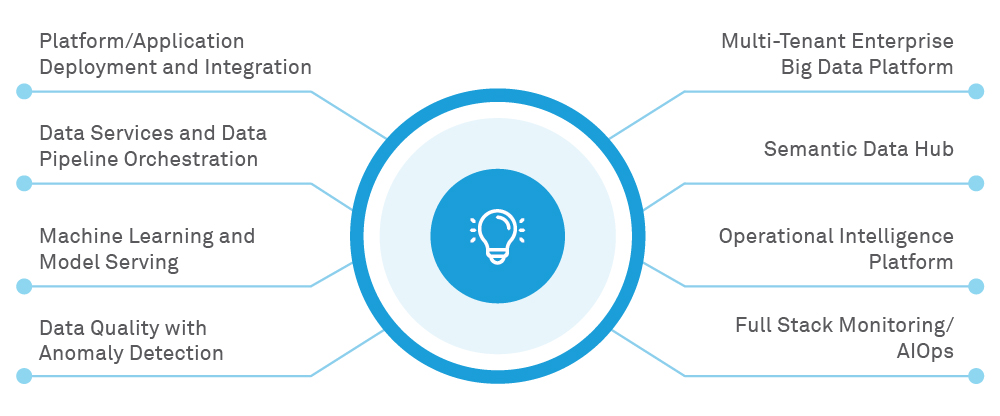
Figure 2: Examples of service industry cloud offerings
As insurers continue to adopt cloud technologies, their focus will move towards PaaS and SaaS services to deploy such fraud models. This would remove reliance on internal technology resources so that the business can focus on adding value to its customers and evolving business models. Figure 3 summarizes what part of your organization could start moving to the cloud and start reaping the benefits from day 1.

Figure 3: Cloud Strategy: Which part of your organization could move to the cloud?
Institutions that have started by moving core systems onto the cloud, plan to carefully follow with a move of their data platforms (including fraud models, reporting and data quality) onto the cloud. The future of “Cloud Only” technology and data platforms is inevitable; it will lead to innovative and efficient ways of solving business problems.
Reimagining the future with cloud
The success of banking and financial institutions are often constrained by its legacy business models. With the advent of advanced, cutting-edge cloud computing technologies, big data, advanced analytics, social data, IoT, AI, conversational bots, financial institutions have changed. They have become more responsive and at the same time, converting cloud investments into a palatable price and product offering advantage. Smart and virtual banking, digital wallet, mobile payments, P2P lending and investments and many more have raised digital transformation to a new level. Cloud technologies and edge computing, together with geo-location and real-time assets monitoring capabilities have given significant new dimensions. As a result, the entire financial risk and decisions can serve their consumers better at an affordable price.
Cloud helps in laying the computation and operating model foundation for the new digital business model. Embracing the evolution of application design, behavioral profiling and significant rise of AI-fused process and products, cloud ecosystem helps to tame the increased demand for specialized ML IaaS and PaaS platforms. Technology and data platforms, founded by a well-defined cloud strategy, that follows innovative platform OpEx models and is digitally scalable and elastic, will reimagine the financial institutions’ success in the future.
Are you facing issues with expensive legacy platforms, the need to process vast volumes of data in real-time, and meeting customer demand for digital / omni-channel experience? Click here to connect with us and find out how we can empower your journey towards being an intelligent financial hub.
Sukhvinder Phalora
Director with the Data, Analytics & AI Consulting practice
He has more than 18 years’ experience within the Financial Services Data domain.
Soumen Chatterjee
Partner with Analytics and AI Consulting, Data, Analytics & AI, Wipro.
Soumen helps organizations become data-centric and adopt the right technologies like cloud, advanced analytics, ML, AI, and IoT to improve their business performance.